Jason Box knows ice. That’s why what’s happened this year concerns him so much.
Box just returned from a trip to Greenland. Right now, the ice there is … black:
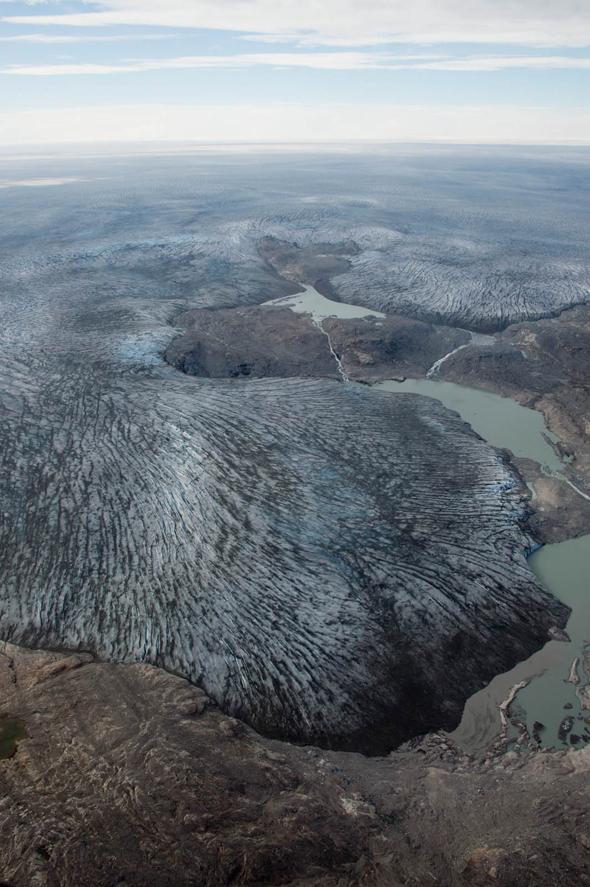

Dark ice is helping Greenland’s glaciers retreat.
Photo by Jason Box

Crevasses criss-cross the Greenland ice sheet, allowing melt water to descend deep beneath the ice.
Photo by Jason Box

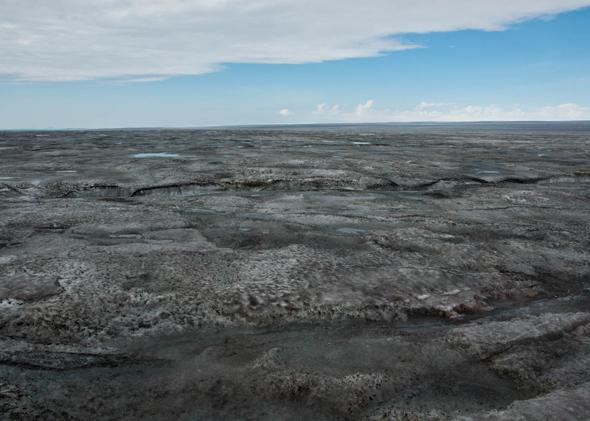
This year, Greenland’s ice was the darkest it’s ever been.
Photo by Jason Box

Box and his team are trying to discover what made this year’s melt season so unusual.
Photo by Jason Box

Box marks his study sites, appropriately, with black flags.
Photo by Jason Box

Box’s ‘Dark Snow’ project is the first scientific expedition to Greenland to be crowdfunded.
Photo by Jason Box
The ice in Greenland this year isn’t just a little dark—it’s record-setting dark. Box says he’s never seen anything like it. I spoke to Box by phone earlier this month, just days after he returned from his summer field research campaign.
“I was just stunned, really,” Box told me.
The photos he took this summer in Greenland are frightening. But their implications are even more so. Just like black cars are hotter to the touch than white ones on sunny summer days, dark ice melts much more quickly.
As a member of the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland, Box travels to Greenland from his home in Copenhagen to track down the source of the soot that’s speeding up the glaciers’ disappearance. He aptly calls his crowdfunded scientific survey Dark Snow.
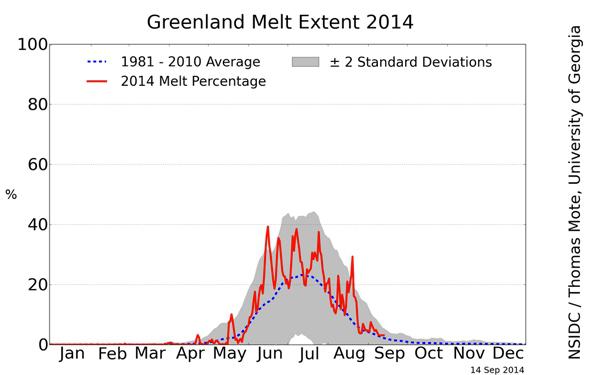
This year was another above-average melt season in Greenland.
Courtesy of The National Snow and Ice Data Center
There are several potential explanations for what’s going on here. The most likely is that some combination of increasingly infrequent summer snowstorms, wind-blown dust, microbial activity, and forest fire soot led to this year’s exceptionally dark ice. A more ominous possibility is that what we’re seeing is the start of a cascading feedback loop tied to global warming. Box mentions this summer’s mysterious Siberian holes and offshore methane bubbles as evidence that the Arctic can quickly change in unpredictable ways.
This year, Greenland’s ice sheet was the darkest Box (or anyone else) has ever measured. Box gives the stunning stats: “In 2014 the ice sheet is precisely 5.6 percent darker, producing an additional absorption of energy equivalent with roughly twice the US annual electricity consumption.”
Perhaps coincidentally, 2014 will also be the year with the highest number of forest fires ever measured in Arctic.
Box ran these numbers exclusively for Slate, and what he found shocked him. Since comprehensive satellite measurements began in 2000, never before have Arctic wildfires been as powerful as this year. In fact, over the last two or three years, Box calculated that Arctic fires have been burning at a rate that’s double that of just a decade ago. Box felt this finding was so important that he didn’t want to wait for peer review, and instead decided to publish first on Slate. He’s planning on submitting these and other recent findings to a formal scientific journal later this year.
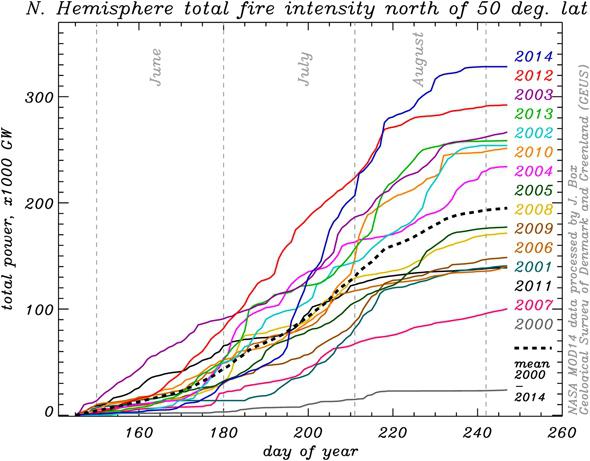
Arctic and sub-Arctic fires were more powerful in 2014 than ever recorded before.
Photo by Jason Box/NASA
Box’s findings are in line with recent research that shows the Arctic is in the midst of dramatic change.
A recent study has found that, as the Arctic warms, forests there are turning to flame at rates unprecedented in the last 10,000 years. This year, those fires produced volumes of smoke and soot that Box says drifted over to Greenland.
In total, more than 3.3 million hectares burned in Canada’s Northwest Territories alone this year—nearly 9 times the long term average—resulting in a charred area bigger than the states of Connecticut and Massachusetts combined. That figure includes the massive Birch Creek Complex, which could end up being the biggest wildfire in modern Canadian history. In July, it spread a smoke plume all the way to Portugal.
In an interview with Canada’s National Post earlier this year, NASA scientist Douglas Morton said, “It’s a major event in the life of the earth system to have a huge set of fires like what you are seeing in Western Canada.”
Box says the real challenge is to rank what fraction of the soot he finds on the Greenland ice is from forest fires, and what is from other sources, like factories. Box says the decline of snow cover in other parts of the Arctic (like Canada) is also exposing more dirt to the air, which can then be more easily transported by the wind. Regardless of their ultimate darkening effect on Greenland, this year’s vast Arctic fires have become a major new source of greenhouse gas emissions from the thawing Arctic. Last year, NASA scientists found “amazing” levels of carbon dioxide and methane emanating from Alaskan permafrost.
Earlier this year, Box made headlines for a strongly worded statement along these lines:
That tweet landed Box in a bit of hot water with his department, which he said now has to approve his media appearances. Still, Box’s sentiment is inspiring millions. His “f’d” quote is serving as the centerpiece of a massive petition (with nearly 2 million signatures at last count) that the activist organization Avaaz will deliver to “national, local, and international leaders” at this month’s global warming rally in New York City on Sept. 21.
